redisRedis源码分析(adlist)
代长亚源码版本:redis-4.0.1
源码位置:
一、adlist简介
Redis中的链表叫adlist(A generic doubly linked list implementation 一个通用的双端链表实现),和普通单链表相比,它的方向可以向前或者向后,这是由于数据结构中定义了next和prev两个指针决定的,下面看下它的数据结构实现。
二、数据结构定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| typedef struct listNode {
struct listNode *next; //next指针,指向下一个元素
struct listNode *prev; //prev指针,指向上一个元素
void *value; //void *类型的数据域
} listNode;
typedef struct list {
struct listNode *head; //head指针指向链表头部
struct listNode *tail; //tail指针指向链表尾部
void *(*dup)(void *ptr); //自定义的复制函数,如果不定义,默认策略的复制操作会让原链表和新链表共享同一个数据域
void (*free)(void *ptr); //自定义free操作
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key); //search操作的时候比较两个value是否相等,默认策略是比较两个指针的值
unsigned long len; //记录链表的长度,获取长度操作可以O(1)返回
} list;
|
三、创建、头插、查找、反转输出、复制、拼接
老规矩,我们还是以一个例子来分析源码,这个例子中会设计到adlist的创建、头插、查找、反转输出、复制、拼接这些操作,例子的代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| int keyMatch(void *ptr, void *key) {
return strcmp(ptr, key) == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
void printList(list *li) {
printf("li size is %d, elements:", listLength(li));
listIter iter;
listNode *node;
listRewind(li, &iter);
while ((node = listNext(&iter)) != NULL) {
printf("%s ", (char*)node->value);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char b[][10] = {"believe", "it", "or", "not"};
listIter iter;
listNode *node;
list *li = listCreate();
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(b)/sizeof(*b); ++i) {
listAddNodeHead(li, b[i]);
}
printList(li);
printf("\nSearch a key :\n");
listSetMatchMethod(li, keyMatch);
listNode *ln = listSearchKey(li, "believe");
if (ln != NULL) {
printf("find key is :%s\n", (char*)ln->value);
} else {
printf("not found\n");
}
printf("\nReverse output the list :\n");
printf("li size is %d, elements:", listLength(li));
listRewindTail(li, &iter);
while ((node = listNext(&iter)) != NULL) {
printf("%s ", (char*)node->value);
}
printf("\n");
printf("\nduplicate a new list :\n");
list *lidup = listDup(li);
printList(lidup);
printf("\nConnect two linked lists :\n");
listJoin(li, lidup);
printList(li);
listRelease(li);
return 0;
}
Out >
li size is 4, elements:not or it believe
Search a key :
find key is :believe
Reverse output the list :
li size is 4, elements:believe it or not
duplicate a new list :
li size is 4, elements:not or it believe
Connect two linked lists :
li size is 8, elements:not or it believe not or it believe
|
list *li = listCreate(); 创建了一个list,并且返回了指针,代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| list *listCreate(void)
{
struct list *list;
if ((list = zmalloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL)
return NULL;
list->head = list->tail = NULL;
list->len = 0;
list->dup = NULL;
list->free = NULL;
list->match = NULL;
return list;
}
|
listAddNodeHead(li, b[i]);然后将预先定义好的数组元素依次头插入了list,与之对应的还有一个尾插的函数listAddNodeTail(),我们先看下头插listAddNodeHead()的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
if (list->len == 0) {
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
node->prev = list->tail;
node->next = NULL;
list->tail->next = node;
list->tail = node;
}
list->len++;
return list;
}
|
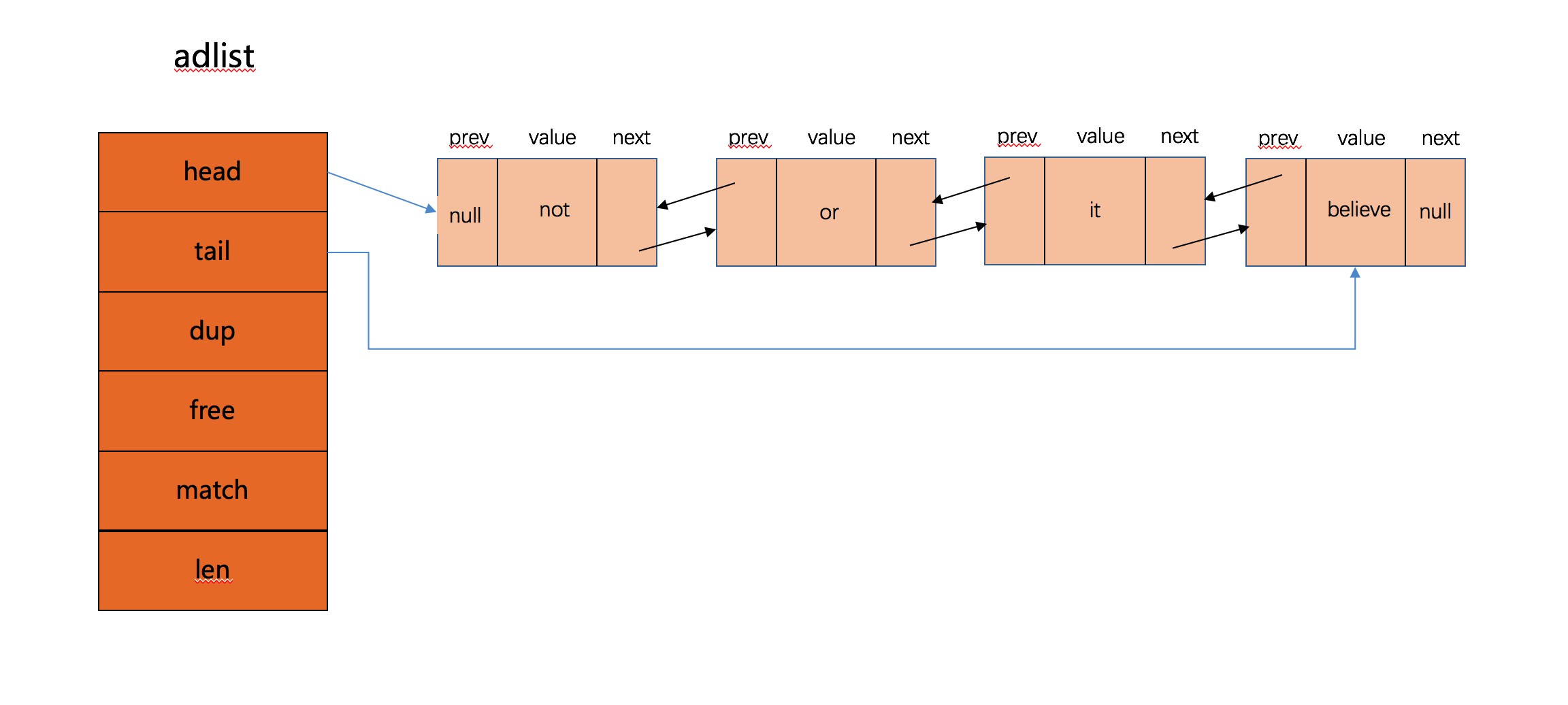
函数首先申请了一个listNode节点,然后用list->len == 0判断了是不是首节点,然后根据不同的策略交换指针,将元素头插入链表,将长度增加,循环插入所有元素之后链表目前情况如下图所示:

listNode *ln = listSearchKey(li, "believe");可以查找第二个参数指定的字符串,默认的匹配原则是比较指针是否相等,但是可以自定义match函数,因为我们的例子中需要比较字符串,我自定义了keyMatch函数如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| match函数的声明是:int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
int keyMatch(void *ptr, void *key) {
return strcmp(ptr, key) == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
|
listSetMatchMethod(li, keyMatch);可以指定match函数,下面我们看下listSearchKey()函数的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| listNode *listSearchKey(list *list, void *key)
{
listIter iter;
listNode *node;
listRewind(list, &iter);
while((node = listNext(&iter)) != NULL) {
if (list->match) {
if (list->match(node->value, key)) { //如果用户自定义了比较函数,就直接使用
return node;
}
} else {
if (key == node->value) { //默认的比较策略是比较指针
return node;
}
}
}
|
因为adlist是双端链表,所以翻转操作十分简单,我们直接将迭代器初始化成从链表尾部开始遍历就完成了翻转操作。
1
| listRewindTail(li, &iter); //将迭代器从尾部迭代
|
list *lidup = listDup(li);会创建一条新的链表返回给用户,但是需要注意默认的复制策略,如果用户不自定义dup()函数,默认返回的复制链表和原始链表共用相同的数据节点,这样对于一个节点修改会导致原始链表发生变化。如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| list *lidup = listDup(li); //使用默认的复制操作
strncpy(listIndex(lidup, 0)->value, "abc", 3); //修改复制返回的链表的值
printList(lidup);
printList(li);
Out >
li size is 4, elements:abc or it believe
li size is 4, elements:abc or it believe //可以看到原始链表也受了影响,not 修改为了 abc
|
但是如果自定义dup函数,不再使得复制之后的链表和原始链表公用节点就可以避免这个问题:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| void *strDup(void *ptr) {
return sdsnew(ptr);
}
listSetDupMethod(li, strDup); //设置自定义的dup函数
list *lidup = listDup(li);
strncpy(listIndex(lidup, 0)->value, "abc", 3);
printList(lidup);
printList(li);
Out >
li size is 4, elements:abc or it believe
li size is 4, elements:not or it believe //还是原始的值没有变化
|
listJoin(li, lidup);可以将两个链表做连接操作:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| void listJoin(list *l, list *o) {
if (o->head)
o->head->prev = l->tail; //将第二个链表链在第一个链表后边
if (l->tail)
l->tail->next = o->head;
else
l->head = o->head;
l->tail = o->tail;
l->len += o->len;
/* Setup other as an empty list. */
o->head = o->tail = NULL;
o->len = 0;
}
|
listRelease(li);函数负责释放链表,首先会调用listEmpty()函数释放掉所有listNode,最后再释放掉list本身的空间。
四、总结
adlist的实现相对来说较简单,我们上面分析了它的创建、插入、查找、反转等操作,基本上熟悉了API和底层数据结构的原理,但是由于链表新增节点时候(无论头插尾插)每次都是申请新的空间,所以比较容易造成内存碎片。这方面想想有无办法优化。
[完]